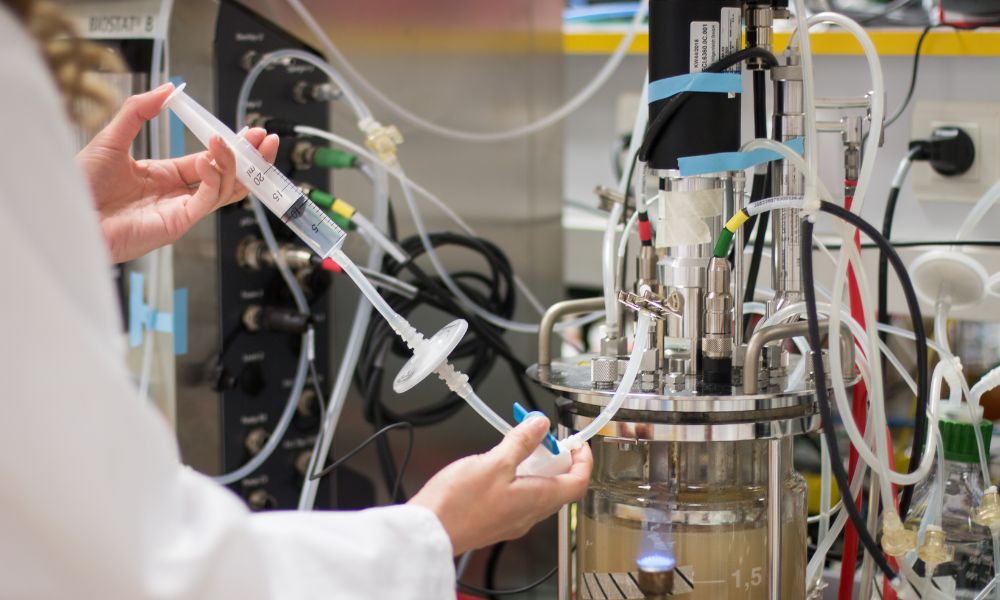
Due to their unique advantages and inherent limitations, single-use bioreactors (SUBs) have become increasingly popular in the bioprocessing industry. Read on to learn the benefits and drawbacks of single-use bioreactors.
Benefits of Single-Use Bioreactors
One of the primary benefits of SUBs is the reduction in sterilization and cleaning requirements. Unlike traditional stainless-steel bioreactors, SUBs eliminate the need for complex cleaning-in-place (CIP) and sterilization-in-place (SIP) systems. Therefore, they significantly reduce preparation time and risk of contamination. This feature makes them particularly advantageous for small-scale productions and processes requiring quick turnarounds.
Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment for a single-use system might be lower than traditional bioreactors, the cost-effectiveness of SUBs is particularly noticeable in reduced operational costs. They don’t require extensive cleaning and sterilization processes, saving time and resources. This aspect is especially beneficial for companies running multiple small batches or developing processes where flexibility and speed are crucial.
Environmental Considerations
The environmental impact of SUBs is a double-edged sword. On one hand, they reduce water and chemical usage in cleaning, positively impacting the environment. However, the single-use nature of these bioreactors means they generate more waste, as the plastic bags and components aren’t reusable. This aspect poses environmental concerns, especially regarding waste management and sustainability.
Limitations in Sensor Technology
While SUBs have advanced sensor technology, they still face limitations in sensor variety and robustness compared to traditional bioreactors. This can sometimes lead to challenges in closely monitoring and controlling intricate bioprocess parameters, which are crucial for sensitive and complex biological productions.
Impact on Scaling Bioprocesses
Scaling up bioprocesses comes with challenges, but SUBs offer significant flexibility. They allow for rapid scale ups or scale downs without extensive modifications to the existing setup. This adaptability is particularly advantageous for companies that need to adjust production volumes frequently or expedite the transition from development to commercial-scale production. However, scaling with SUBs may also present challenges in replicating the exact process conditions at larger scales, requiring careful planning and validation.
Now that you know the benefits and drawbacks of single-use bioreactors, you can better assess their suitability for your bioprocessing needs. While they offer significant advantages in flexibility and reduced operational costs, you must consider their environmental impact and certain technical limitations to make informed decisions in bioprocess engineering.